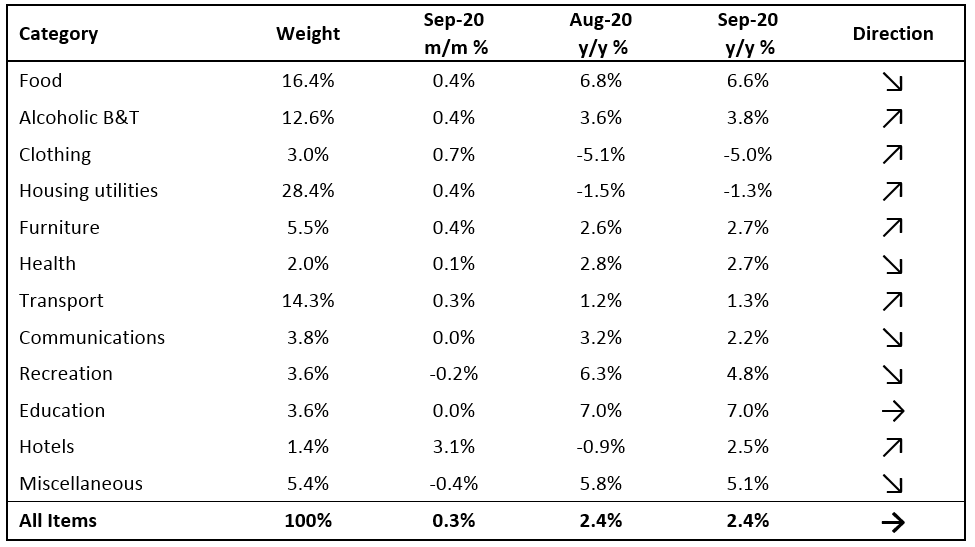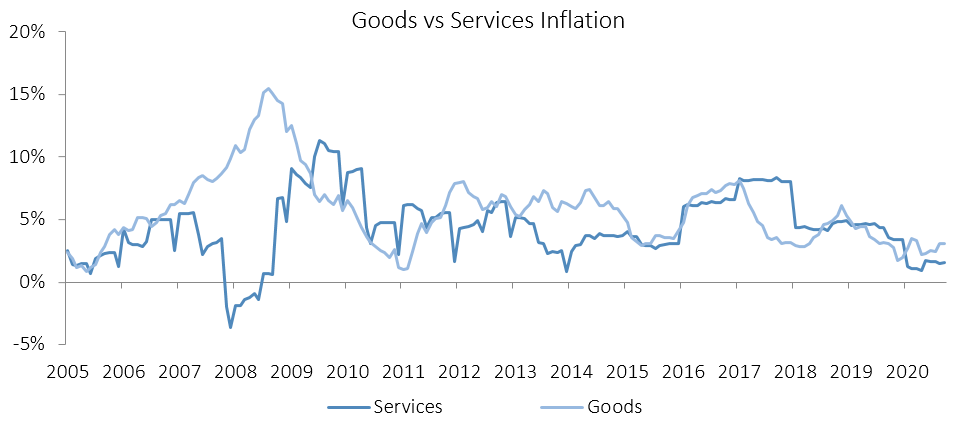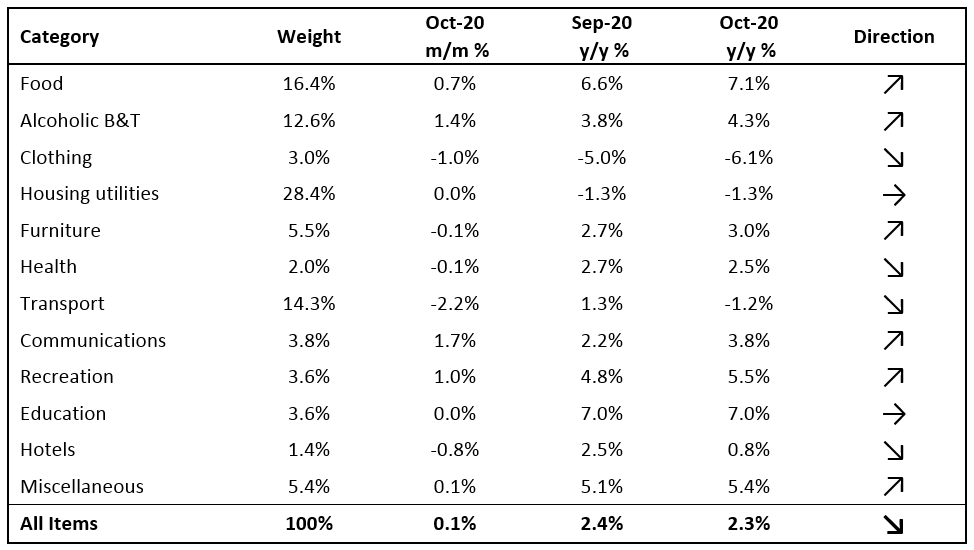
The Namibian annual inflation rate remained relatively steady at 2.3% y/y in October, following the 2.4% y/y uptick in prices in September. Prices in the overall NCPI basket increased by 0.1% m/m, as inflationary pressure remains muted. On a year-on-year basis, overall prices in six of the twelve basket categories rose at a quicker rate in October than in September, while four categories recorded slower rates of inflation and two categories posted steady inflation. Prices for goods increased by 3.3% y/y while prices for services rose by 0.9% y/y.
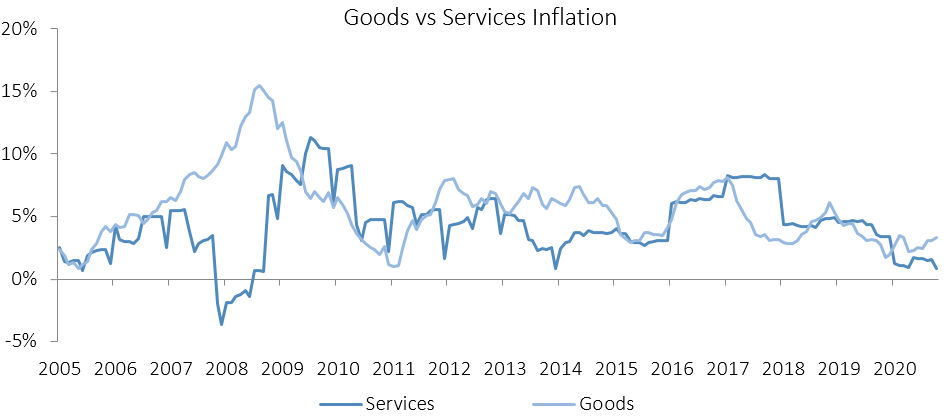
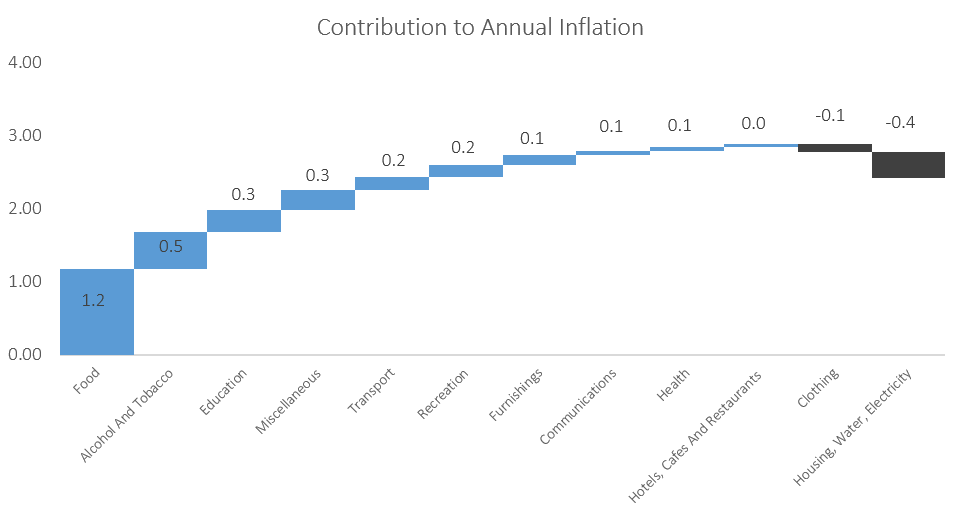
As in September, food & non-alcoholic beverages were the largest contributors to annual inflation in October, accounting for 1.3 percentage points of the total 2.3% annual inflation rate. Prices in this category rose 0.7% m/m and 7.1% y/y, the highest level since March 2017. Prices in all thirteen sub-categories recorded increases on a year-on-year basis with the largest increases being observed in the prices of fruits which increased by 16.1% y/y and vegetables which increased by 14.1% y/y. Price increases in meat products and fish also remained elevated at 9.3% y/y and 8.5% y/y respectively. The prospects for the Southern African region to receive normal to above-normal rainfall for the 2020-21 cropping season are currently high as La Niña conditions is expected to be sustained until at least February 2021. Should this materialise, food inflation should slow down.
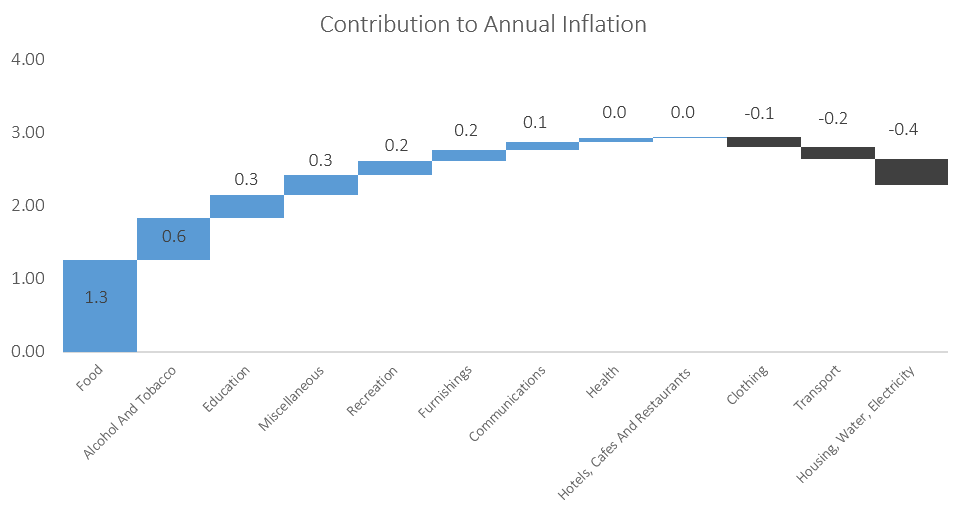
The alcoholic beverages and tobacco basket item was the second largest contributor to the annual inflation rate in October. The basket item recorded a price increase of 1.4% m/m and 4.3% y/y during the month. Prices for alcoholic beverages increased at a rate of 1.0% m/m and 3.4% y/y, while tobacco prices rose by 3.2% m/m and 8.4% y/y.
The education basket recorded inflation of 7.0% y/y, with the cost of pre-primary education growing at a rate of 5.6%. Primary and secondary education recorded price increases of 9.3% y/y, while tertiary education prices rose by 5.3% y/y. None of the three subcategories printed price increases on a month-on-month basis. The fact that the basket item with the eighth largest weighting (at 3.6% of the CPI basket) is one of the largest contributors of the annual inflation rate is an indication of just how low inflationary pressure is at the moment.
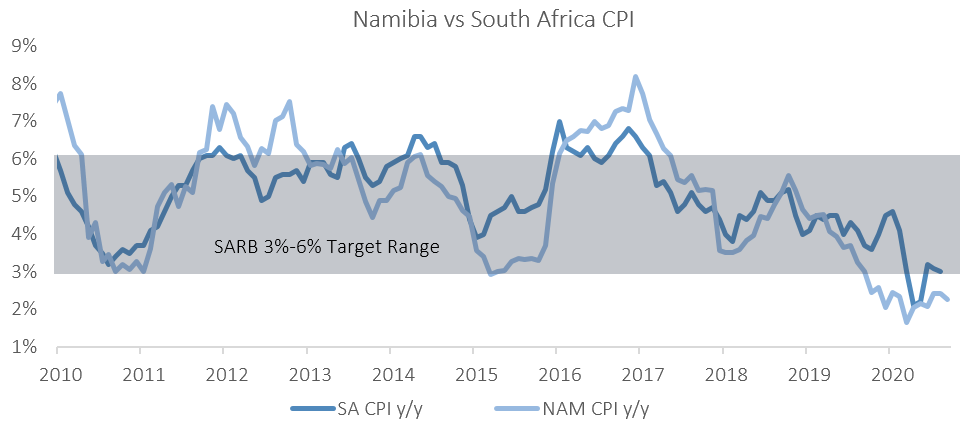
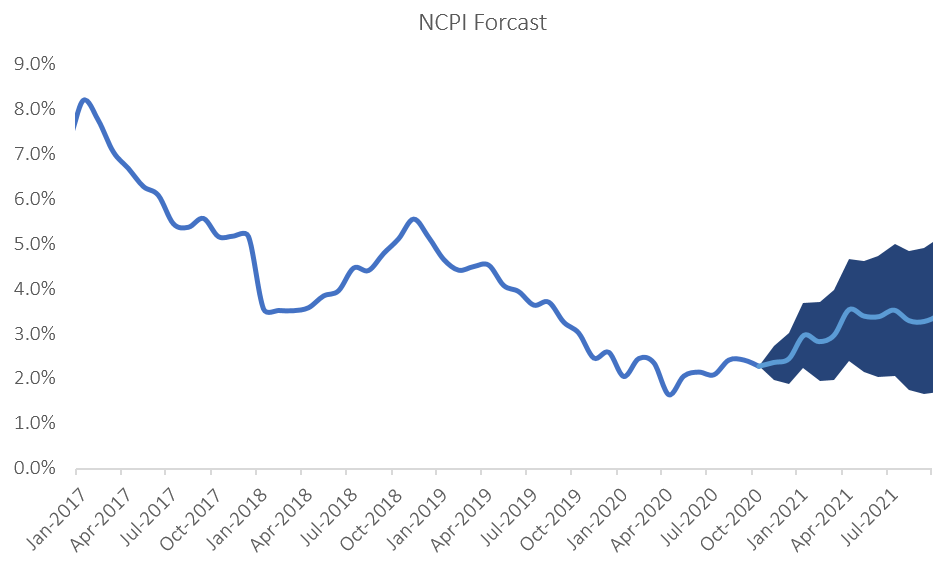
We believe that inflationary pressure will remain relatively contained at around current levels in the short-term. IJG’s inflation model forecasts an average inflation rate of 2.2% y/y in 2020 and 3.4% y/y in 2021. One of the larger risks to our inflation forecast is global oil prices. While there has been an uptick in oil prices in recent weeks, it is improbable that it would return to levels seen at the beginning of the year anytime soon as the global demand for oil remains muted, especially since several European countries are implementing renewed lockdown measures. The likelihood of higher rental prices in the next 12 months also remains low, given the financial pressure many consumers are under. With these being the larger categories of the inflation basket, we do not foresee any sudden increases in Namibian inflation in the short-term.