Overall
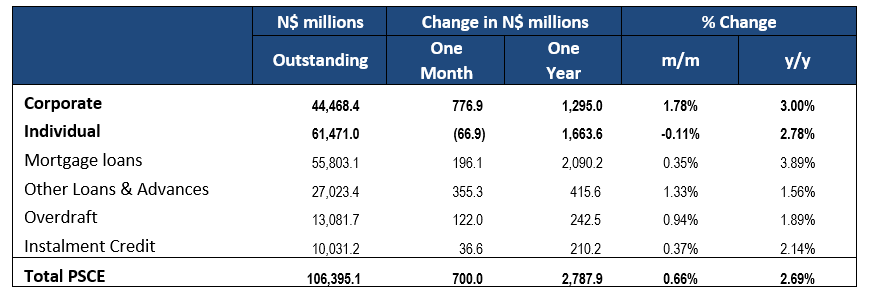
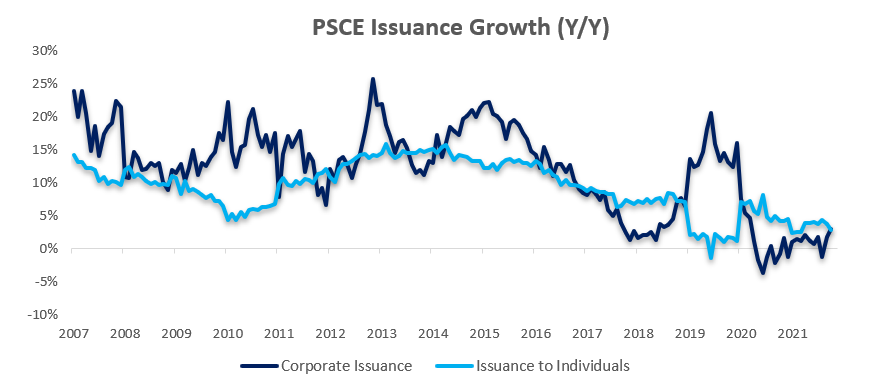
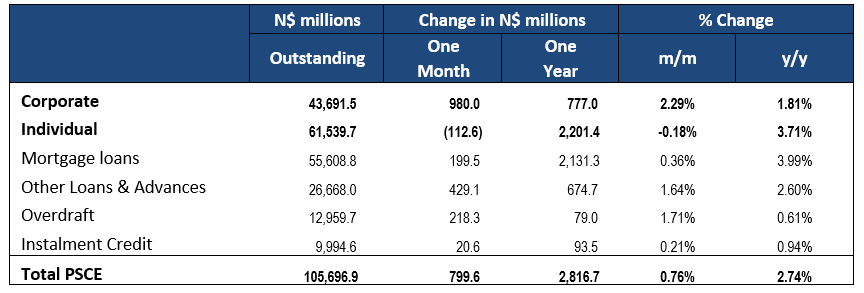
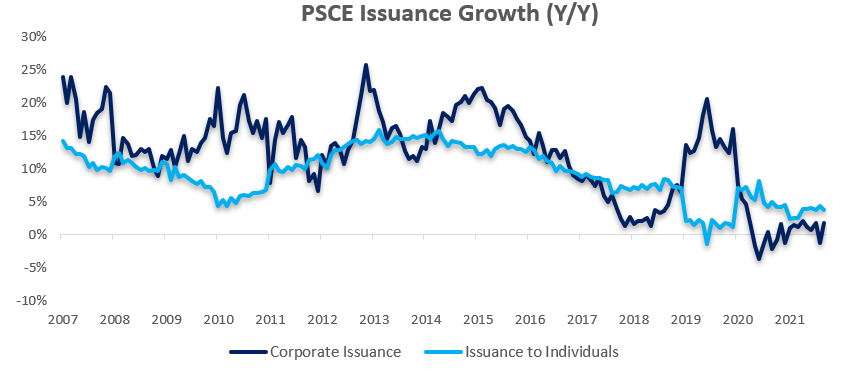
Private sector credit (PSCE) increased by N$337.1 million or 0.32% m/m in November, bringing the cumulative credit outstanding to N$106.7 billion. On a year-on-year basis, private sector credit increased by 1.56% in November, down from growth of 2.69% y/y in October. On a 12-month cumulative basis N$1.64 billion worth of credit was extended to the private sector. Individuals continue to constitute the majority of the cumulative issuance.

Credit Extension to Individuals
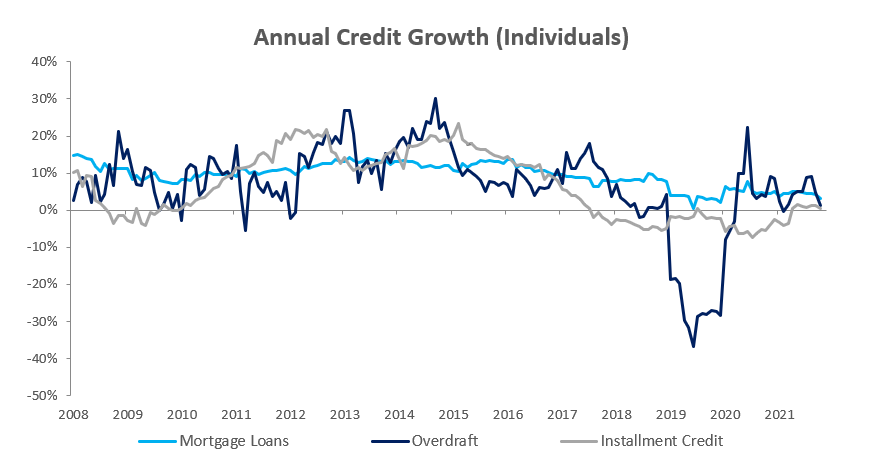
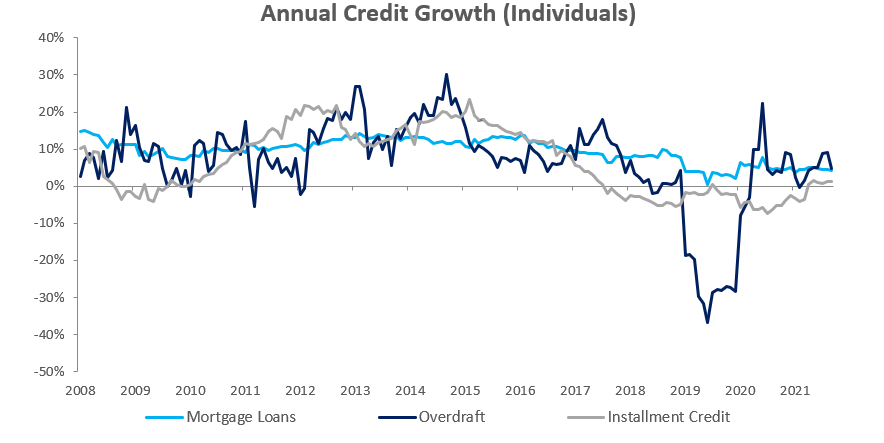
Credit extended to individuals increased by 0.5% m/m after two consecutive months of contractions. On a year-on-year basis, credit extended to individuals rose by 2.55% in November. On a month-on-month basis, other loans and advances’ (consisting of credit card debt, personal- and term loans) increased by 0.2% m/m. Mortgage loans and overdrafts also recorded minor growth at 0.7% m/m and 0.1% m/m, respectively. Instalment credit shrunk by 0.4% m/m. On a year-on-year basis all subcategories of loans & advances, bar overdrafts, posted increases in November. Overdrafts contracted by 3.8% y/y in November. Mortgage loans increased by 3.4% y/y and other loans and advances grew by 2.3% y/y.

Credit Extension to Corporates
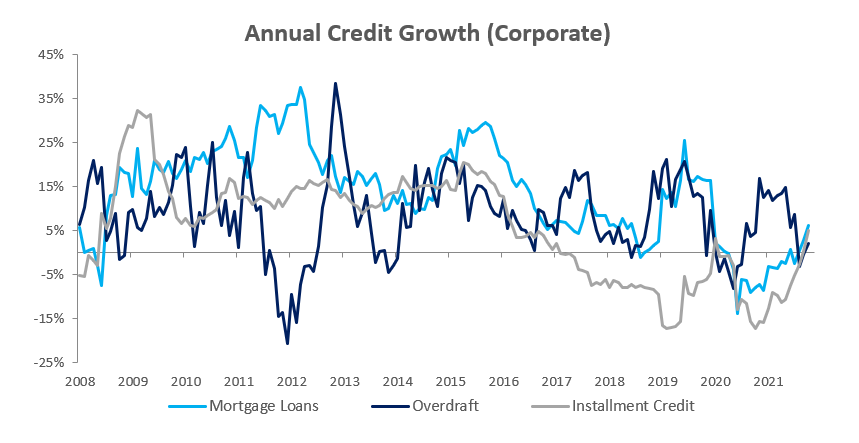
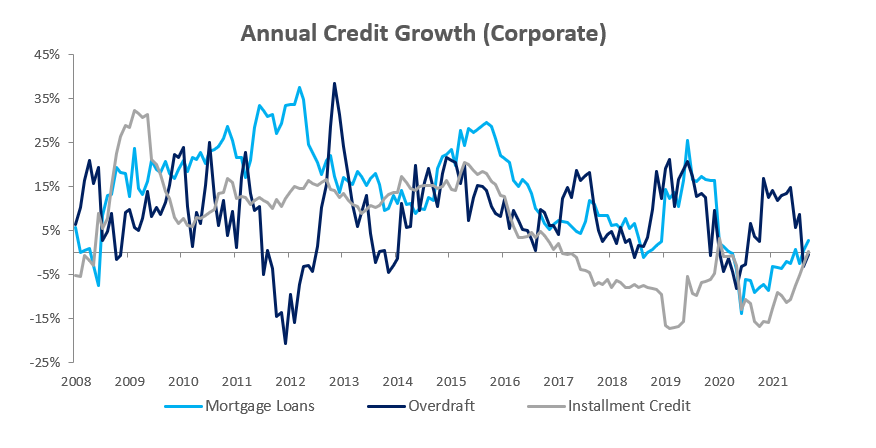
Credit extended to corporates grew by 0.17% m/m and 0.62% y/y in November. Total corporate loans & advances contracted by 0.2% m/m. Mortgage loans grew by 0.8% m/m, other loans and advances grew by 0.2% m/m. Overdrafts declined by 2.3% m/m. Instalment credit grew by 4.1% m/m, the largest increase since June 2019. The trend is broadly similar on year-on-year basis. Total corporate loans & advances remained steady in November, with all sub-categories except overdrafts recording increases.

Banking Sector Liquidity
The overall liquidity position of Namibia’s commercial banks increased in November, rising by N$1.61 billion to an average of N$3.84 billion. The BoN attributes the increase to cash inflows from asset managers, as well as inflows from the subscription of MTC shares. The repo balance rose to N$393.7 million at the end of the month after ending October at N$200.9 million.

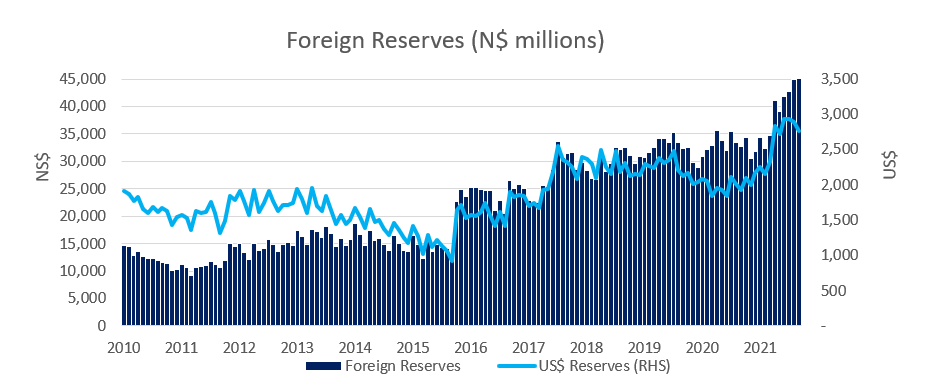
Reserves and Money Supply
Broad Money Supply (M2) increased by N$3.50 billion or 2.8% y/y in November, according to the BoN’s latest monetary statistics. The money supply increased by 0.8% m/m, increasing to N$129.9 billion after ending October at N$128.8 billion. The BoN’s stock of international reserves contracted by 14.3% m/m to N$41.0 billion in November. The large decline was due to the redemption of the Eurobond as well as commercial bank foreign currency purchases during the month, according to the BoN.

Outlook
Overall, PSCE growth remained subdued and in line with what has been seen so far in 2021. The rolling 12-month issuance is down 41.3% y/y to N$1.64 billion. Credit extended to corporates as well as individuals have displayed a similar sluggish trend to that of 2020. This reflects the current lack of optimism in the Namibian economy. Despite providing relief to strained businesses and individuals alike, historically low interest rates have failed to achieve notable economic stimulus. As such, PSCE is expected to remain relatively flat in the near-term.