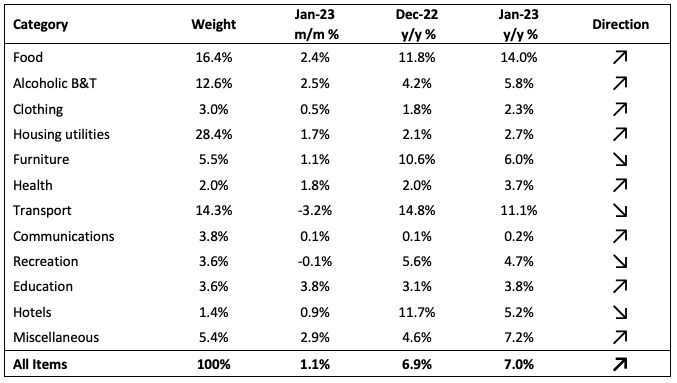
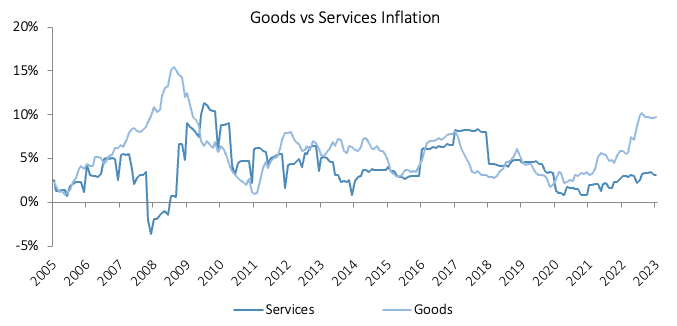
The Namibian annual inflation rate rose to 7.0% y/y in January on the back of the 6.9% y/y increase in prices recorded in December. On a monthly basis, prices in the overall NCPI basket rose by 1.1%, compared to a 0.3% m/m increase in December. On a year-on-year basis, overall prices in eight of the twelve basket categories rose at a quicker rate in January than in December, while the other four recorded slower rates of inflation. Prices for goods increased by 9.8% y/y while prices for services rose by 3.1% y/y.
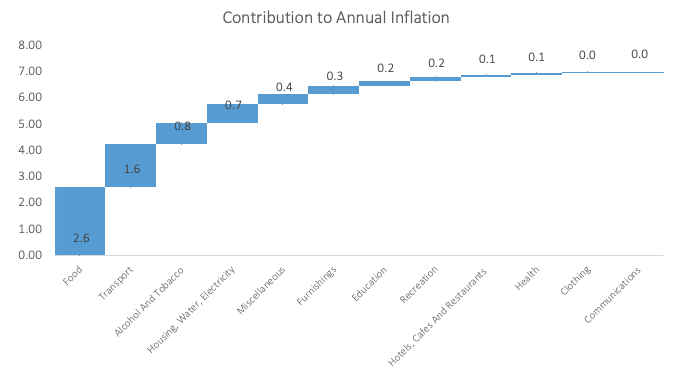
Inflation Attribution
Food and non-alcoholic beverages prices rose 14.0% in January from a year earlier. The basket category, accounting for 16.4% of the NCPI basket , contributed 2.6 percentage points to the annual inflation rate in January. This marks the first month since August 2021 that the transport category was not the top contributor to the annual inflation rate. Month-on-month food and non-alcoholic prices rose by 2.4%, the highest since March 2016. Fruit price inflation ticked up for a second consecutive month to 22.3% y/y, with citrus prices rising by 23.8% y/y, grapes by 6.7% y/y and avocados logging 64.2% y/y. The prices of breads and cereals rose by 3.0% m/m and 22.3% y/y, emanating from maize prices that are 37.2% higher than a year ago, and bread- and cake flour being 27.1% more expensive. The only sub-category to record slower inflation on an annual basis than last month was ‘oils and fats’ which posted inflation of 16.8% y/y, the lowest since March 2022.
Transport was the second largest contributor to January’s annual inflation print, contributing 1.64 percentage points. Prices in this category rose by 11.1% y/y, the lowest since October 2021. On a month-on-month basis, transport prices fell by 3.2%, following the Ministry of Mines and Energy’s decision to lower the prices of both petrol and diesel in the beginning of January. This resulted in the operation of personal transport equipment inflation slowing to 15.9% y/y from the 22.6% recorded in December. The Ministry’s decision in the beginning of February to leave fuel prices unchanged should aid to further ease price pressure in this category. Prices of the purchase of vehicles sub-category ticked up for a fourth consecutive month to 1.3% m/m and 6.2% y/y. Public transportation services inflation remained relatively steady month-on-month and eased to 0.9% y/y from 1.4% in December.
The alcohol and tobacco category posted inflation of 2.5% m/m and 5.8% y/y. The prices of alcoholic beverages climbed by 3.0% m/m and 6.5% y/y. The acceleration from December’s 4.5% y/y rate was mainly driven by the prices of white spirits that are 24.7% higher than a year ago. Tobacco products recorded price increases of 0.2% m/m and 2.7% y/y, with cigarette prices up 5.3% y/y while pipe tobacco prices are down 4.2% y/y.
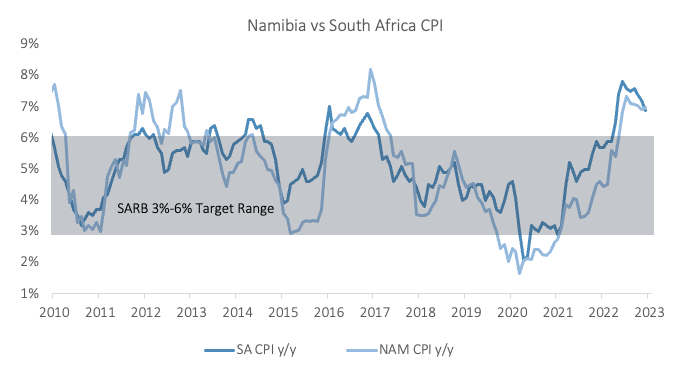
Outlook
Namibia’s annual inflation rate of 7.0% in January came in moderately higher than South Africa’s rate of 6.9%, for the first time since April 2019. Lower fuel prices helped to tame inflationary pressure, but stubbornly high food inflation (the highest since March 2009 on an annual basis) continued to put upward pressure on the overall inflation print.
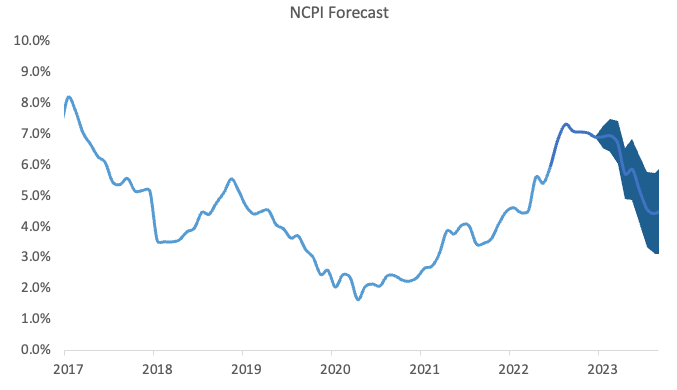
While the housing, water & electricity category’s contribution to the annual rate, at 0.7 percentage points, was relatively low, it is worth noting that the prices for the rental payments for dwellings subcategory rose by 2.1% y/y from 1.4% y/y previously. As rental payments make up a large portion (23.3%) of the CPI basket, the low inflationary adjustment means that Namibia’s annual inflation is likely to moderate throughout the year, provided that transport inflation continues to slow. IJG’s inflation model currently forecasts Namibia’s annual inflation rate to steadily slow during the course of 2023, before reaching around 4.3% at the end of the year.
The Bank of Namibia (BoN) in its monetary policy committee today (15 February 2023) raised the repo rate by a further 25bps to 7.00%, in line with the SARB’s hike in January. Forward-rate agreements, which are used to speculate on future borrowing costs, show traders are pricing in one more 25 basis-point increase by the SARB in the current rate-hiking cycle. Should the BoN follow suit, it will take the Namibian repo rate to 7.25%, the highest since May 2009.