A total of 91 building plans were approved by the City of Windhoek in December, which is a 51.1% m/m decline from the 186 plans approved in November. In value terms, however, approvals increased by 34.6% m/m to register N$166.4 million worth of approvals in December compared to N$123.6 million in November. A total of 45 buildings with a total value of N$36.4 million were completed during December, representing declines of 82.5% m/m and 84.5% m/m in the number and value of completions, respectively. A total of 2,032 building plans were approved in 2019, 86 fewer than in 2018. However, in value terms approvals increased by 8.3% in 2019, rising to N$1.99 billion from N$1.84 billion in 2018.

Additions to properties once again made up the majority of building plans approved in 2019. Of the 2,032 building plans approved in 2018, additions accounted for 1,630 of those approvals, 35 more than in 2018. In value terms however, approvals of additions for the year declined by N$151.2 million or 16.3% y/y. The value of additions approved has been contracting for the past four years, with the 2019 decline of 16.3% following the 13.5% contraction recorded in 2018. 65 additions were approved in December, 100 fewer than in November and 62.1% lower in value terms at N$32.8 million. During the year, 1,275 additions have been completed to a value of N$689.5 million, a drop of 43.9% y/y in number and 8.1% y/y in value.
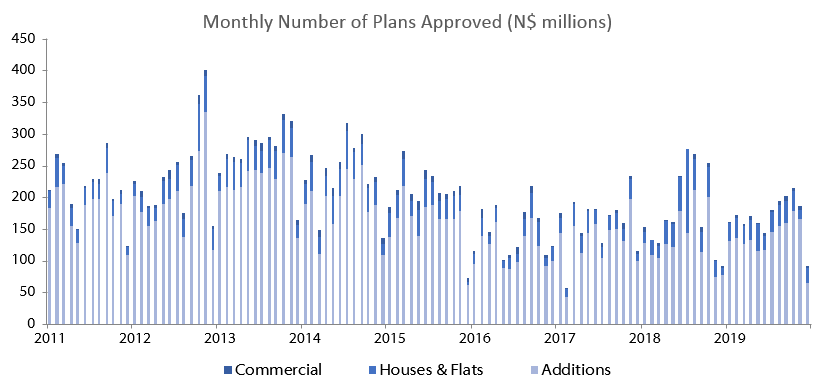
New residential units were the second largest contributor to the total number of building plans approved with 355 approvals registered in 2019, 125 less than in 2018. In value terms new residential units approved increased from N$532.2 million in 2018 to N$640.8 million in 2019. On a month-on-month basis, the number of new residential approvals increased by 43.8% to 23 in December, while the value of approvals increased by 338.4% to N$123.0 million. This increase in value is mostly due to a single large residential approval of N$77.0 million in Khomasdal. 29 Residential units valued at N$29.5 million were completed in December, bringing 2019’s total number to 308, up 280.2% y/y, and value to N$409.5 million, up 290.8% y/y.
A total of 47 commercial and industrial units were approved in 2019 compared to the 43 approved in 2018. In value terms, commercial and industrial approvals rose by N$195.3 million or 51.4% for the year in 2019 from the N$380.3 million reported in 2018. On a month-on-month basis, a total of three commercial and industrial projects worth N$10.65 million were approved in December, representing a 40.0% m/m reduction in terms of number, but an increase of 16.4% m/m in terms of value. No commercial and industrial buildings were completed in December, leaving 2019’s number of completed buildings in this category unchanged at 29, an 81.3% y/y increase. In value terms, N$185.5 million worth of commercial and industrial units were completed in 2018, representing an increase of 249.9% y/y.
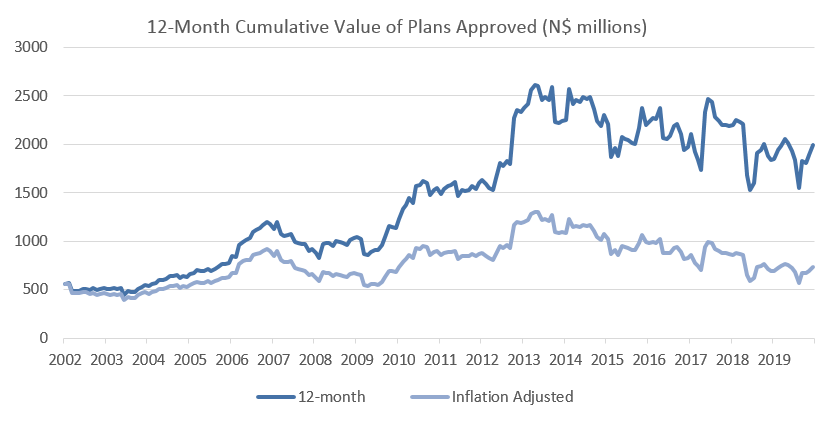
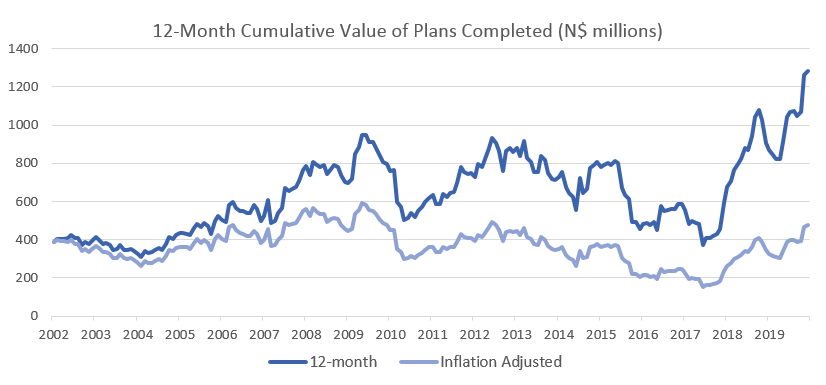
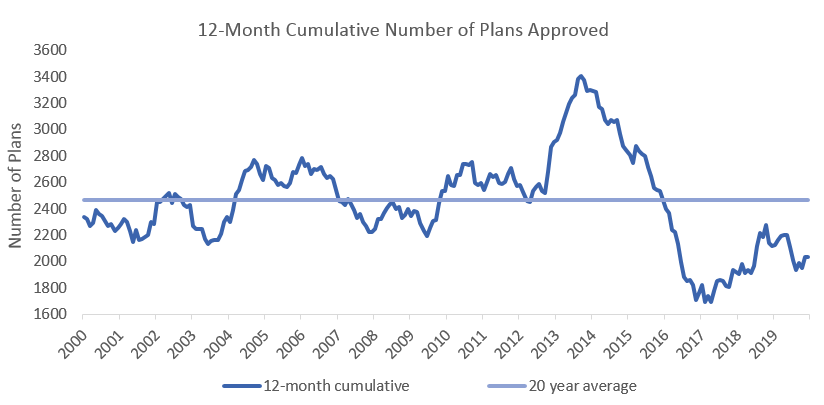
The number of building plans approved in 2019 declined by 4.1% compared to 2018 and the cumulative number of plans is down 40.3% from its peak in 2013. Although there has been an 8.3% y/y increase in the cumulative value of approvals to N$1.99 billion in 2019, the cumulative value of approvals is still down 23.6% from the peak in 2013 in nominal terms. Building plans approved is a leading indicator of economic activity in the country and the above data implies that the Namibian economy is still showing signs of hardship. The value of plans completed has however recovered more significantly during 2019 as can be seen in the below figure.